Introduction to China’s AI-AI-Appearance Transport Leip
In 2025, China aims to replace its urban transit infrastructure by rolling out completely autonomous, AI-managed driverless buses in major cities. This initiative is a milestone in search of the country to become a global leader in smart transportation and AI application. With ambitious technical integration and urban dynamics innovation, China is not just catching up—it is leaping into the future.
What Are Driverless Buses? A Technological Primer
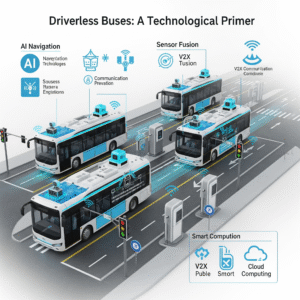
Driverless buses or autonomous buses are vehicles that operate without the involvement of a human driver, they are operated by systems containing AI, GPS, sensors and real time data analysis.
Core technologies behind autonomous buses
- Lidar and radar sensors—maps detect converts and objects.
- Computer Vision – Traffic processes the signal, pedestrians, and dangers.
- Artificial Intelligence-RIC-Time Driving decides.
- Cloud connectivity—enables continuous updates and remote diagnostics.
How to enable AI and machine learning for safe driving
These systems continuously train on road behavior, recognize patterns in traffic, and refine decisions with deep learning models. The more buses run, the cleverer it becomes—reducing human error and optimizing the routes
Why 2025 Is a Milestone Year for China’s Smart Cities

Government policies and five year plans
China’s 14th Fifth year (2021–2025) emphasizes AI, green energy, and intelligent infrastructure. The Ministry of Transport has dozens of pilot projects and encourages public-private participation.
Urbanization and the Need for Smart Transit
With over 60% of China’s population living in urban areas, traffic congestion and pollution are growing concerns. Driverless buses offer a scalable, low-emission solution.
Pilot Projects Already in Motion

Case Study: Shenzhen’s Self-Driving Bus Trial
In Shenzhen, autonomous buses operate on select routes using 5G for navigation and real-time adjustments. Passenger feedback shows improved punctuality and safety.
Beijing’s AI-Integrated Public Bus Experience
Beijing launched AI-assisted buses with facial recognition for ticketing, autonomous navigation, and even AI traffic management integration.
Environmental Benefits of Driverless Electric Buses
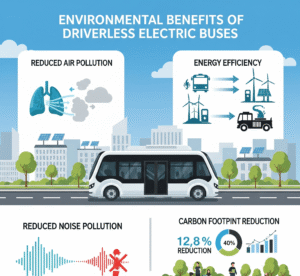
Electric, driverless buses reduce greenhouse gas emissions and noise pollution substantially. China has not only embraced these buses as part of its “Blue Sky” initiative but has also promoted them in the context of its carbon neutrality goals by 2060.
Benefits of an autonomous bus system in urban areas

An autonomous bus is a bus that operates driverless on adapted routes based on real-time traffic data and passenger demand. Decreased waiting time, eliminating traffic congestion, and more spontaneous transport in a dense population are possible in urban settings.
Public reaction and passenger experience so far
- Security, comfort and access
- Most passengers report an easy experience.
- Characteristics such as automated wheelchair ramps, voice-command interactions, and safety alerts increase inclusion.
- Real-time tracking apps give full control and transparency to users.
Economic Effects: Jobs, Startup and Market Price
While some jobs may phase out, new roles in AI maintenance, cybersecurity, and transport analytics are booming. China’s autonomous bus market is projected to exceed $30 billion by 2030, creating an innovation-driven economy.
Challenges in Scale Driverless Bus Network
- legal, moral and infrastructure obstacles
- In case of accidents unclear legal liabilities
- 5G and smart infrastructure requires
- Public beliefs and moral dilemmas (e.g., accident decision)
Global Competition: How China gets piled up
- China competes with the US, the European Union, and South Korea in the autonomous vehicle race.
- However, its centralized governance and large urban population get a unique benefit in rolling out infrastructure-water innovations quickly.
The Role of 5G and IoT in Enabling Autonomy
Driverless buses rely on ultra-fast 5G for:
- Vehicle-to Vahana (V2V) communication
- Detection
-
Cloud updates and software enhancements
-
The IoT framework ensures buses communicate with city traffic systems, stops, and even smart streetlights.
The Future of Transportation in China Post-2025
Integration with Smart Grids and Smart Cities
Driverless buses will become key nodes in smart cities, connecting with electric grids for charging, using blockchain for transparent data logging, and AI for real-time mobility decision-making.
Expert opinion and industry forecast
Experts of Baidu, Huawei, and China Association of Automobile Manufacturers estimate a rate of 40% adoption of driverless public transport in Tier 1 cities by 2030. McKins’ predicted an average reduction of 15 minutes in pilot cities.
FAQs
1. Are driverless buses already operational in China?
Yes, currently the pilot programs are in Shenzhen and in Beijing, with future plans for an large expansion in 2025.
2. How safe are autonomous buses?
These buses work with multi-level sensor technology and AI decision-making (machine learning), resulting in less accidents than human-powered buses.
3. Will this technology displace driver jobs?
Some roles may change but overall there will be new technology related jobs in maintenance, data analytics and systems.
4. Can driverless buses work with different seasons?
The modern fleets don‘t have a problem dealing with medium weather. Testing is still taking place for extreme weather.
5. Is 5G required for these buses?
Yes, 5G is a real-time data exchange that enables safe, efficient navigation.
6. Where can I ride a driverless bus in China?
Try routes in Shenzhen or the Hydian district of Beijing. Both have autonomous bus services open to the public.
Conclusion
China’s bold vision for 2025 and beyond includes a wise, autonomous transport ecosystem, where driverless buses again shape how people run. Leading the allegations with AI, 5G, and IOT, the nation has been well deployed to bring revolution in public mobility and to create smart, green cities.
